Blog & Latest Updates
Fly Fishing Articles
Insects by Common Name


Mayfly Genus Baetis (Blue-Winged Olives)
Taxonomic Navigation -?-
Kingdom
Animalia (Animals)
» Phylum
Arthropoda (Arthropods)
» Class
Insecta (Insects)
» Order
Ephemeroptera (Mayflies)
» Family
Baetidae (Blue-Winged Olives)
» Genus Baetis (Blue-Winged Olives)
17 species aren't included.
Common Names
This is page 3 of specimens of Baetis. Visit the main Baetis page for:
- The behavior and habitat of Baetis.
Pictures of 32 Mayfly Specimens in the Genus Baetis:
Female Baetis (Blue-Winged Olives) Mayfly Dun View 4 PicturesI'm guessing this specimen is in the genus Acerpenna because of the very sharp costal process (
View 4 PicturesI'm guessing this specimen is in the genus Acerpenna because of the very sharp costal process (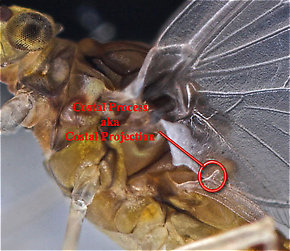 Costal process: A bump or point sticking up from the front margin of an insect's wing, usually the rear wing of certain mayflies. It is sometimes called a costal projection.) on her hind wing. I'm guessing pygmaea because it is the most common species.
Costal process: A bump or point sticking up from the front margin of an insect's wing, usually the rear wing of certain mayflies. It is sometimes called a costal projection.) on her hind wing. I'm guessing pygmaea because it is the most common species.
Editor note: Not Acerpenna. This is most likely Baetis. See comments on this male specimen for rationale. Also compare with the female specimen associated with it.
 View 4 PicturesI'm guessing this specimen is in the genus Acerpenna because of the very sharp costal process (
View 4 PicturesI'm guessing this specimen is in the genus Acerpenna because of the very sharp costal process (
The costal process of a Baetidae dun.
Editor note: Not Acerpenna. This is most likely Baetis. See comments on this male specimen for rationale. Also compare with the female specimen associated with it.
Collected July 1, 2005 from the Bois Brule River in Wisconsin
Added to Troutnut.com by Troutnut on April 22, 2006
Added to Troutnut.com by Troutnut on April 22, 2006
Male Baetis bicaudatus (BWO) Mayfly Nymph View 7 PicturesThis specimen was collected along with a female which was quite a bit larger, different in color, but otherwise seemed the same morphologically.
View 7 PicturesThis specimen was collected along with a female which was quite a bit larger, different in color, but otherwise seemed the same morphologically.
 View 7 PicturesThis specimen was collected along with a female which was quite a bit larger, different in color, but otherwise seemed the same morphologically.
View 7 PicturesThis specimen was collected along with a female which was quite a bit larger, different in color, but otherwise seemed the same morphologically.Collected April 12, 2021 from Holder Creek in Washington
Added to Troutnut.com by Troutnut on April 13, 2021
Added to Troutnut.com by Troutnut on April 13, 2021
Female Baetis bicaudatus (BWO) Mayfly Nymph View 12 PicturesI collected this one along with a male that was quite a bit smaller but equally ready to emerge in mid April.
View 12 PicturesI collected this one along with a male that was quite a bit smaller but equally ready to emerge in mid April.
I spent (Spent: The wing position of many aquatic insects when they fall on the water after mating. The wings of both sides lay flat on the water. The word may be used to describe insects with their wings in that position, as well as the position itself.) quite a while on the identifications, because they really don't look very much like the Baetis bicaudatus nymph I caught last year in Idaho. However, the presence of hind wing pads ( Wing pad: A protrusion from the thorax of an insect nymph which holds the developing wings. Black wing pads usually indicate that the nymph is nearly ready to emerge into an adult.) rules out Acentrella turbida, the lack of a fringe of long setae (Seta: Little hairs on insects.) on the tibiae (
Wing pad: A protrusion from the thorax of an insect nymph which holds the developing wings. Black wing pads usually indicate that the nymph is nearly ready to emerge into an adult.) rules out Acentrella turbida, the lack of a fringe of long setae (Seta: Little hairs on insects.) on the tibiae ( Tibia: A middle segments in the leg of an insect, located between the femur and the tarsus.) rules out Acentrella insignificans, range rules out Heterocloeon and Iswaeon, and the thumb-like projection on the labial palp (
Tibia: A middle segments in the leg of an insect, located between the femur and the tarsus.) rules out Acentrella insignificans, range rules out Heterocloeon and Iswaeon, and the thumb-like projection on the labial palp (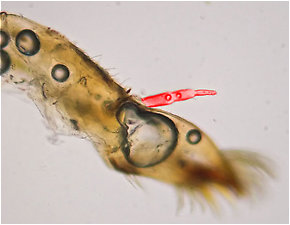 Palp: A long, thin, often segmented appendage which can protrude from certain insect mouth parts such as the maxillae. Also known as the < />palpus.) points to Baetis. Thus, Baetis bicaudatus is a fairly confident ID, and it's not too surprising that it looked different from my previous specimen because bicaudatus is thought to be a species complex with multiple types that haven't been fully sorted out yet.
Palp: A long, thin, often segmented appendage which can protrude from certain insect mouth parts such as the maxillae. Also known as the < />palpus.) points to Baetis. Thus, Baetis bicaudatus is a fairly confident ID, and it's not too surprising that it looked different from my previous specimen because bicaudatus is thought to be a species complex with multiple types that haven't been fully sorted out yet.
The microscope pictures for this specimen aren't from the same exact nymph, but a mixture of a few others of the same kind that I didn't mind dissecting.
 View 12 PicturesI collected this one along with a male that was quite a bit smaller but equally ready to emerge in mid April.
View 12 PicturesI collected this one along with a male that was quite a bit smaller but equally ready to emerge in mid April.I spent (Spent: The wing position of many aquatic insects when they fall on the water after mating. The wings of both sides lay flat on the water. The word may be used to describe insects with their wings in that position, as well as the position itself.) quite a while on the identifications, because they really don't look very much like the Baetis bicaudatus nymph I caught last year in Idaho. However, the presence of hind wing pads (

The wing pads on this final instar Baetidae mayfly nymph are extremely dark.

The tibia of this Isonychia bicolor mayfly spinner is highlighted in red.

The palp on the maxilla of an Ephemerella nymph (detached and photographed under a microscope) is highlighted in red here.
The microscope pictures for this specimen aren't from the same exact nymph, but a mixture of a few others of the same kind that I didn't mind dissecting.
Collected April 12, 2021 from Holder Creek in Washington
Added to Troutnut.com by Troutnut on April 13, 2021
Added to Troutnut.com by Troutnut on April 13, 2021
Male Baetis tricaudatus (Blue-Winged Olive) Mayfly Nymph View 14 PicturesThis specimen and many like it were found with other specimens I found to be duller-colored females of the same species. I wasn't aware of such a difference between male and female nymphs in Baetids, but all the morphological characteristics I checked in the key were the same, and the color patterns are, too -- just not the brightness.
View 14 PicturesThis specimen and many like it were found with other specimens I found to be duller-colored females of the same species. I wasn't aware of such a difference between male and female nymphs in Baetids, but all the morphological characteristics I checked in the key were the same, and the color patterns are, too -- just not the brightness.
 View 14 PicturesThis specimen and many like it were found with other specimens I found to be duller-colored females of the same species. I wasn't aware of such a difference between male and female nymphs in Baetids, but all the morphological characteristics I checked in the key were the same, and the color patterns are, too -- just not the brightness.
View 14 PicturesThis specimen and many like it were found with other specimens I found to be duller-colored females of the same species. I wasn't aware of such a difference between male and female nymphs in Baetids, but all the morphological characteristics I checked in the key were the same, and the color patterns are, too -- just not the brightness.Collected April 9, 2021 from the Yakima River in Washington
Added to Troutnut.com by Troutnut on April 12, 2021
Added to Troutnut.com by Troutnut on April 12, 2021
Female Baetis tricaudatus (Blue-Winged Olive) Mayfly Nymph View 13 PicturesThese nymphs were highly abundant in my early April kick net samples from the Yakima Canyon, and one of them emerged into a dun, which I photographed immediately. Similar-looking nymphs but with distinctly brighter color patterns were also abundant. I just photographed one. After extensive views under the microscope, it's clear the bright ones are males and the dull ones are females of the same species.
View 13 PicturesThese nymphs were highly abundant in my early April kick net samples from the Yakima Canyon, and one of them emerged into a dun, which I photographed immediately. Similar-looking nymphs but with distinctly brighter color patterns were also abundant. I just photographed one. After extensive views under the microscope, it's clear the bright ones are males and the dull ones are females of the same species.
The most likely guess at the species is Baetis tricaudatus, which may be a complex of related species that haven't all been sorted out yet. It isn't a perfect fit to every key characteristic (and I never seem to find a Baetis that matches the expected pronotum (Pronotum: The top of the insect prothorax.) color patterns, but that seems to be the closest.
The microscope images here were taken with different specimens from the main photos (so I could dissect them while preserving that one intact), but clearly the same species.
 View 13 PicturesThese nymphs were highly abundant in my early April kick net samples from the Yakima Canyon, and one of them emerged into a dun, which I photographed immediately. Similar-looking nymphs but with distinctly brighter color patterns were also abundant. I just photographed one. After extensive views under the microscope, it's clear the bright ones are males and the dull ones are females of the same species.
View 13 PicturesThese nymphs were highly abundant in my early April kick net samples from the Yakima Canyon, and one of them emerged into a dun, which I photographed immediately. Similar-looking nymphs but with distinctly brighter color patterns were also abundant. I just photographed one. After extensive views under the microscope, it's clear the bright ones are males and the dull ones are females of the same species. The most likely guess at the species is Baetis tricaudatus, which may be a complex of related species that haven't all been sorted out yet. It isn't a perfect fit to every key characteristic (and I never seem to find a Baetis that matches the expected pronotum (Pronotum: The top of the insect prothorax.) color patterns, but that seems to be the closest.
The microscope images here were taken with different specimens from the main photos (so I could dissect them while preserving that one intact), but clearly the same species.
Collected April 9, 2021 from the Yakima River in Washington
Added to Troutnut.com by Troutnut on April 12, 2021
Added to Troutnut.com by Troutnut on April 12, 2021
Baetis (Blue-Winged Olives) Mayfly Nymph View 5 Pictures
View 5 Pictures
 View 5 Pictures
View 5 PicturesCollected April 1, 2007 from Mystery Creek #62 in New York
Added to Troutnut.com by Troutnut on April 3, 2007
Added to Troutnut.com by Troutnut on April 3, 2007
Female Baetis tricaudatus (Blue-Winged Olive) Mayfly Dun View 9 PicturesThis dun emerged on my desk from a container of nymphs I was sorting, so I was able to get an ID from the nymphs. I also uploaded photos of a female nymph and a male nymph.
View 9 PicturesThis dun emerged on my desk from a container of nymphs I was sorting, so I was able to get an ID from the nymphs. I also uploaded photos of a female nymph and a male nymph.
 View 9 PicturesThis dun emerged on my desk from a container of nymphs I was sorting, so I was able to get an ID from the nymphs. I also uploaded photos of a female nymph and a male nymph.
View 9 PicturesThis dun emerged on my desk from a container of nymphs I was sorting, so I was able to get an ID from the nymphs. I also uploaded photos of a female nymph and a male nymph.Collected April 9, 2021 from the Yakima River in Washington
Added to Troutnut.com by Troutnut on April 11, 2021
Added to Troutnut.com by Troutnut on April 11, 2021
Baetis (Blue-Winged Olives) Mayfly Nymph View 4 Pictures
View 4 Pictures
 View 4 Pictures
View 4 PicturesCollected April 14, 2007 from Cayuta Creek in New York
Added to Troutnut.com by Troutnut on April 22, 2007
Added to Troutnut.com by Troutnut on April 22, 2007
Baetis tricaudatus (Blue-Winged Olive) Mayfly Nymph View 20 PicturesA nymph of the same species as this one emerged into a dun in my studio so I got photos of both stages.
View 20 PicturesA nymph of the same species as this one emerged into a dun in my studio so I got photos of both stages.
NOTE: I missed an important key characteristic the first time I tried to identify this one (robust setae (Seta: Little hairs on insects.) on the abdominal sternites ( Sternite: The bottom (ventral) part of a single segment on an insect's abdomen.), which were harder to see than I expected but are clearly present), so I went on a bit of a wild goose chase and landed at a dead end. After spotting that characteristic, this one keys more straightforwardly to either Baetis tricaudatus or the Baetis piscatoris complex. It doesn't seem to be a perfect fit for either one in the key, but I'm going with tricaudatus based on range and abundance. It's not certain.
Sternite: The bottom (ventral) part of a single segment on an insect's abdomen.), which were harder to see than I expected but are clearly present), so I went on a bit of a wild goose chase and landed at a dead end. After spotting that characteristic, this one keys more straightforwardly to either Baetis tricaudatus or the Baetis piscatoris complex. It doesn't seem to be a perfect fit for either one in the key, but I'm going with tricaudatus based on range and abundance. It's not certain.
However, I'm leaving the flawed analysis below with this disclaimer, because some aspects of how I approached that dead end might be informative in the future.
----Incorrect analysis below----
After spending a lot of time with this one under my shiny new microscope, I'm still not quite sure what it is. I botched my attempt to expose the mouth parts that might make the ID more definitive. Based on the key in Webb et al 2018's "Baetis Larvae of North America," here's my reasoning at each key couplet.
Couplet 1. The pronotum (Pronotum: The top of the insect prothorax.) lacks dark, submedian U-shaped markings. Also, if I were to follow through to couplet 2, there seem to be characteristics that rule out each of the options: the intercalaris complex is ruled out by the abdominal markings, and the caudal (Caudal: Toward the posterior tip of the body.) filaments have neither a dark median band (ruling out the flavistriga complex) nor uniform pale coloration (ruling out Baetis notos). This sends me with decent confidence to couplet 4.
Couplet 4. I cannot find robust setae (Seta: Little hairs on insects.) in my microscope on the scapes, pedicels, paraprocts, or sterna. I also do not see a pair of dark, bilobed markings on the pronotum (Pronotum: The top of the insect prothorax.). Unless I overlooked these characteristics, proceed to couplet 9.
Couplet 9. Abdominal tergum (Tergum: the dorsal part of an abdominal segment or segments (terga). Also used to describe the entire abdominal dorsum or the thoracic dorsal segments of Odonata.) 5 is a bit paler than adjacent terga (Tergum: the dorsal part of an abdominal segment or segments (terga). Also used to describe the entire abdominal dorsum or the thoracic dorsal segments of Odonata.), but "distinctly paler"? The figure for Baetis alius in the paper, as well as a very nice picture posted by Millcreek in the forum here, shows that Baetis alius would have darker tergites ( Tergite: The top (dorsal) part of a single segment on an insect's abdomen when it consists of a single chitinous plate (sclerite), or an individual sclerite if the segment has more than one.) surrounding #5. So proceed to couplet 11.
Tergite: The top (dorsal) part of a single segment on an insect's abdomen when it consists of a single chitinous plate (sclerite), or an individual sclerite if the segment has more than one.) surrounding #5. So proceed to couplet 11.
Couplet 11. The length of the gills is obviously less than 2X their width. This leads to the Baetis vernus complex, which could include that species or Baetis brunneicolor. This key doesn't say how to tell those species apart.
Switching over to Burien et al 2018 as the source, the characteristics used to distinguish vernus from brunneicolor seem to rule out either one. Brunneicolor should have more uniformly brown abdominal tergites ( Tergite: The top (dorsal) part of a single segment on an insect's abdomen when it consists of a single chitinous plate (sclerite), or an individual sclerite if the segment has more than one.), whereas vernus should have a lack of visible tracheation in most of the gills.
Tergite: The top (dorsal) part of a single segment on an insect's abdomen when it consists of a single chitinous plate (sclerite), or an individual sclerite if the segment has more than one.), whereas vernus should have a lack of visible tracheation in most of the gills.
The fore femur ( Femur: The main segment of an insect's leg close to the body, in between the tibia and the trochanter.) length is about 3.8x its width.
Femur: The main segment of an insect's leg close to the body, in between the tibia and the trochanter.) length is about 3.8x its width.
Also worth noting: In the genus ID, I thought I could see the villipore in my microscope, but I'm not sure. If I back out of Baetis altogether and assume there's no villipore, I end up at Fallceon, but this specimen doesn't seem to have the frontal keel on the head that's supposed to be present on Fallceon quilleri. So that seems like a dead end as well.
 View 20 PicturesA nymph of the same species as this one emerged into a dun in my studio so I got photos of both stages.
View 20 PicturesA nymph of the same species as this one emerged into a dun in my studio so I got photos of both stages.NOTE: I missed an important key characteristic the first time I tried to identify this one (robust setae (Seta: Little hairs on insects.) on the abdominal sternites (

One sternite of this Isonychia bicolor mayfly spinner is highlighted in red.
However, I'm leaving the flawed analysis below with this disclaimer, because some aspects of how I approached that dead end might be informative in the future.
----Incorrect analysis below----
After spending a lot of time with this one under my shiny new microscope, I'm still not quite sure what it is. I botched my attempt to expose the mouth parts that might make the ID more definitive. Based on the key in Webb et al 2018's "Baetis Larvae of North America," here's my reasoning at each key couplet.
Couplet 1. The pronotum (Pronotum: The top of the insect prothorax.) lacks dark, submedian U-shaped markings. Also, if I were to follow through to couplet 2, there seem to be characteristics that rule out each of the options: the intercalaris complex is ruled out by the abdominal markings, and the caudal (Caudal: Toward the posterior tip of the body.) filaments have neither a dark median band (ruling out the flavistriga complex) nor uniform pale coloration (ruling out Baetis notos). This sends me with decent confidence to couplet 4.
Couplet 4. I cannot find robust setae (Seta: Little hairs on insects.) in my microscope on the scapes, pedicels, paraprocts, or sterna. I also do not see a pair of dark, bilobed markings on the pronotum (Pronotum: The top of the insect prothorax.). Unless I overlooked these characteristics, proceed to couplet 9.
Couplet 9. Abdominal tergum (Tergum: the dorsal part of an abdominal segment or segments (terga). Also used to describe the entire abdominal dorsum or the thoracic dorsal segments of Odonata.) 5 is a bit paler than adjacent terga (Tergum: the dorsal part of an abdominal segment or segments (terga). Also used to describe the entire abdominal dorsum or the thoracic dorsal segments of Odonata.), but "distinctly paler"? The figure for Baetis alius in the paper, as well as a very nice picture posted by Millcreek in the forum here, shows that Baetis alius would have darker tergites (

One tergite of this Isonychia bicolor mayfly spinner is highlighted in red.
Couplet 11. The length of the gills is obviously less than 2X their width. This leads to the Baetis vernus complex, which could include that species or Baetis brunneicolor. This key doesn't say how to tell those species apart.
Switching over to Burien et al 2018 as the source, the characteristics used to distinguish vernus from brunneicolor seem to rule out either one. Brunneicolor should have more uniformly brown abdominal tergites (

One tergite of this Isonychia bicolor mayfly spinner is highlighted in red.
The fore femur (

The femur of this Isonychia bicolor mayfly spinner is highlighted in red.
Also worth noting: In the genus ID, I thought I could see the villipore in my microscope, but I'm not sure. If I back out of Baetis altogether and assume there's no villipore, I end up at Fallceon, but this specimen doesn't seem to have the frontal keel on the head that's supposed to be present on Fallceon quilleri. So that seems like a dead end as well.
Collected September 12, 2020 from the Yakima River in Washington
Added to Troutnut.com by Troutnut on September 19, 2020
Added to Troutnut.com by Troutnut on September 19, 2020
Male Baetis tricaudatus (Blue-Winged Olive) Mayfly Spinner View 12 PicturesSome notes from identifying this specimen under the microscope:
View 12 PicturesSome notes from identifying this specimen under the microscope:
1. The hind wing has three longitudinal veins (Longitudinal vein: Longitudinal veins are the major long veins running length-wise through an insect's wing, connecting the base to the outer margin, or the major branches from those veins.), but the third is faint, short (about half the length of the wing), and close to the wing margin.
2. Then antenna is brown fading into white at the tip, and the base is ringed with white.
3. The joints of the tarsal segments on the middle and hind leg have fine black markings.
It was also collected in association with a female spinner.
 View 12 PicturesSome notes from identifying this specimen under the microscope:
View 12 PicturesSome notes from identifying this specimen under the microscope:1. The hind wing has three longitudinal veins (Longitudinal vein: Longitudinal veins are the major long veins running length-wise through an insect's wing, connecting the base to the outer margin, or the major branches from those veins.), but the third is faint, short (about half the length of the wing), and close to the wing margin.
2. Then antenna is brown fading into white at the tip, and the base is ringed with white.
3. The joints of the tarsal segments on the middle and hind leg have fine black markings.
It was also collected in association with a female spinner.
Collected September 4, 2020 from Silver Creek in Idaho
Added to Troutnut.com by Troutnut on September 18, 2020
Added to Troutnut.com by Troutnut on September 18, 2020
Top 10 Fly Hatches
Top Gift Shop Designs
Eat mayflies.
Top Insect Specimens
Miscellaneous Sites
Troutnut.com is copyright © 2004-2024 Jason
Neuswanger (email Jason). See my FAQ for information about use of my images.
 privacy policy
privacy policy
